Voltage, Current and Resistance
In this topic we have covered the basics of current , voltage and the resistance which are the most fundamental to run any electrical appliances like light and fan .
Voltage :
Voltage is the driving force which allows the electrons to flow.
We can say that voltage is basically a pressure which is pressurizing the electrons to flow in a circuit.
This electrons on the other hand are the flow of current which is there in the circuit .
This current allows the appliances to turn on .
The voltage source can be of two types either it can be a constant voltage source that is also called as DC voltage or else can vary periodically with time which is called as AC voltage
The unit for voltage is called as volts it can also be denoted in sub multiples such as microvolts which is 10^(- 6) volts, millivolts which is 10^(-3) volts.
Voltage can either be positive or negative. In the earlier days voltage was also known as electromotive force or EMF.
And this is the reason why in equation such as Ohm’s law voltage is still represented by the symbol E
Textual definition for voltage is :
“1 volt is the potential difference between two points 1 joule of energy is used to move 1 coulomb of charge from one point to another.”
Crurrent
Current is a movement or just a flow of electrical charge and is measured in amperes which is symbolized by the letter I.
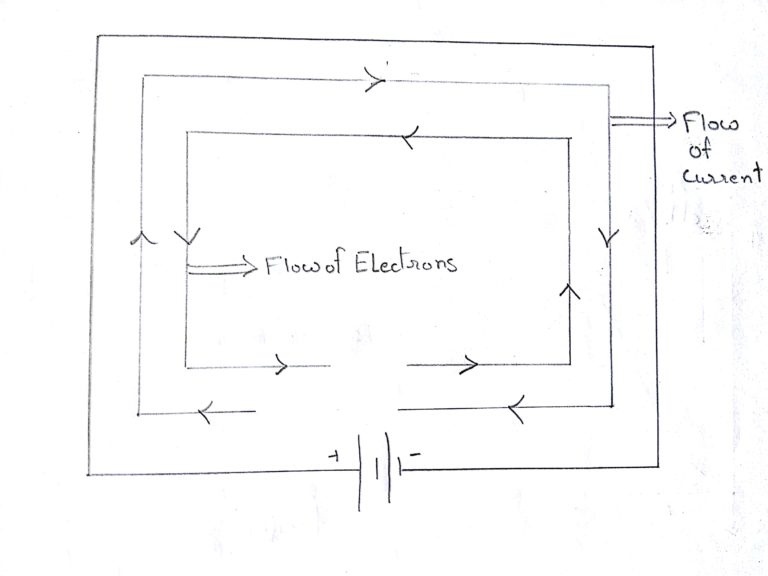
It is the continuous and uniform flow of electrons around a circuit that are being pushed by the voltage source.
In reality electrons flow from negative terminal to the positive terminal of the supply but for the ease of circuit understanding , conventional current flow direction is used this conventional current flow assume that the current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
The textual definition of current is
“Electric current is the flow of electrons.”
The textual definition of Ampere is
“1 Ampere is defined as the current that flows with the electric charge of 1 coulomb for 1 second .”
Resistance :
Till now we have understood that the electricity is basically the flow of current which is being conducted by the voltage in the circuit.
But we all know that the current flows in the circuit through the wires and this wires does not allow the smooth flow of current in the circuit .
Any material will try to resist or prevent the flow of current or more specifically I can say a flow of electric charge within a circuit.
This will lower down the voltage which is being transmitted from the power supply.
Definition of Resistance :
“The capacity of a material to resist or prevent the flow of current or more specifically the flow of electric charge within circuit.”
The element which does this is called as resistor and SI unit of resistance is Ohm
Resistors can be connected either in series or parallel.
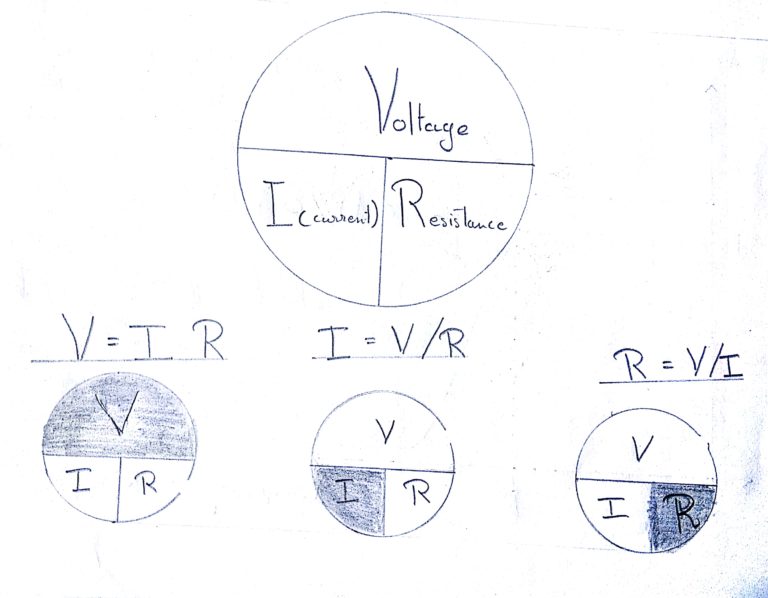
Ohm’s Law :
Georg Ohm found that, at a constant temperature, the electrical current flowing through a fixed linear resistance is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it, and also inversely proportional to the resistance. This relationship between the Voltage, Current and Resistance is defined as Ohms Law .
Formula for Ohm’s Law is
Voltage = Current*Resistance